
NOTE: Click on any image to listen to its audio clip.
Notes
Personal
pronouns in dative case
Personal pronouns in dative case are as follows:
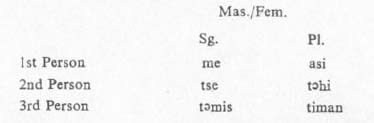
Notice that the second and third person plural
f.mp3s are used for honorific singulars as well. The pronouns do not change for
gender.
Demonstrative
pronouns in dative case
Following are the f.mp3s of the demonstrative
pronouns used with inanimate and animate objects in date case:

The plural f.mp3s are used for honorific singulars
as well.
Dative case
The subjects in dative case are f.mp3ed by adding -as
or -is suffixes to the masculine nouns and the faminine nouns which end
in I. The
suffix -i is added to the faminine nouns:
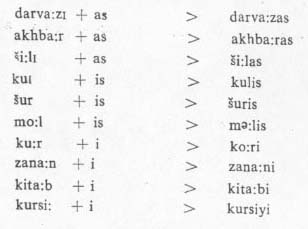
Notice that -as is added to the -I
vowel ending or the consonant ending masculine nouns preceded by low vowel. The
suffix -is is added to the consonant ending masculine nouns which are
preceded by a high or mid back vowel. the suffix -i is added to all other
feminine nouns. As a result of adding of these suffixes, certain morphophonemic
changes occur.
Postpositions
In Kashmiri postpositions are of two types: (1)
Those which follow the nouns in dative case, and (2) those which follow the
nouns in ablative case. In this lesson, we have used the postpositions:
 All
these postpositions follow the subjects in dative case: All
these postpositions follow the subjects in dative case:
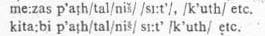
In case postpositions follow a subject phrase
containing a det.mp3iner and noun, both the constituents of the phrase take the
dative case f.mp3s:

Future f.mp3s
of verbs
The following suffixes are added to the consonant
and vowel ending main verb roots for f.mp3ing the future f.mp3s agreeing with the
subject in person and number:

Examples:

|