These
are pronounced with a complete closure in the same way as in Hindi-Urdu
and English. The air pressure builds up behind the closure and is released
with a mild explosion. The stop sounds are of the following three types:
-
the voiceless unaspirated
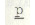 , , 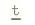 , , 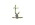 , , 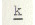 , ,
-
voiceless aspirated
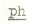 , , 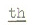 , , 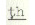 , , 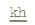 ,
and ,
and
-
voiced unaspirated b,
d,
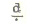 ,
g. ,
g.
On the basis of place
of articulation, these may be further be grouped into four types.
The two lips are the
primary articulators, and these are completely closed. The 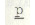 , , 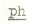 ,
and b are bilabial stops. They are pronounced in the same way as
p,
ph,
and b in such Hindi-Urdu words as pa:ni: 'water',
phu:l
'flower' and bartan 'utensil'. The Kashmiri ,
and b are bilabial stops. They are pronounced in the same way as
p,
ph,
and b in such Hindi-Urdu words as pa:ni: 'water',
phu:l
'flower' and bartan 'utensil'. The Kashmiri 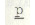 is not aspirated, as in English put, it is like p in spin.
The b is pronounced the same way as the b in English bull
or body.
is not aspirated, as in English put, it is like p in spin.
The b is pronounced the same way as the b in English bull
or body.
The tongue tip articulates
with the upper teeth. The 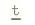 , , 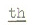 ,
and d are dental stops. They are pronounced in the same way as the
comparable stops in Hindi-Urdu ta:l 'rhythmic beat', tha:na:
'police station', and dard 'pain'. ,
and d are dental stops. They are pronounced in the same way as the
comparable stops in Hindi-Urdu ta:l 'rhythmic beat', tha:na:
'police station', and dard 'pain'.
The tongue tip is curled
back. It articulates with the hard palate. The 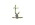 , , 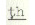 ,
and ,
and 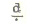 are retroflex stops. These sounds are similar to the initial sounds of
the Hindi-Urdu words
are retroflex stops. These sounds are similar to the initial sounds of
the Hindi-Urdu words 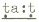 'gunny bag',
'gunny bag', 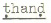 'cold' and
'cold' and 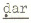 'fear', respectively.
'fear', respectively.
The back of the tongue
articulates with the soft palate. 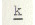 ,
, 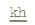 , and
g
are velar stops. These sounds are similar to the initial sounds in the
Hindi-Urdu words ka:m 'work', kha:na: 'food' and ga:na:
'song', respectively. , and
g
are velar stops. These sounds are similar to the initial sounds in the
Hindi-Urdu words ka:m 'work', kha:na: 'food' and ga:na:
'song', respectively.
|